C语言绘制表白玫瑰花教程及源码
点击打开在线编译器,边学边练
一、项目介绍
这是一个用C语言绘制的表白玫瑰花图形。
玫瑰花象征爱情和真挚纯洁的爱,爱情、和平、友谊、勇气和献身精神的化身,人们多把它作为爱情的信物。赶快把它送给你想送的人吧!
编译环境:visual c++ 6.0
第三方库:Easyx2022 注意需要提前安装easyX,如没有基础可以先了解easyX图形编程
二、运行截图
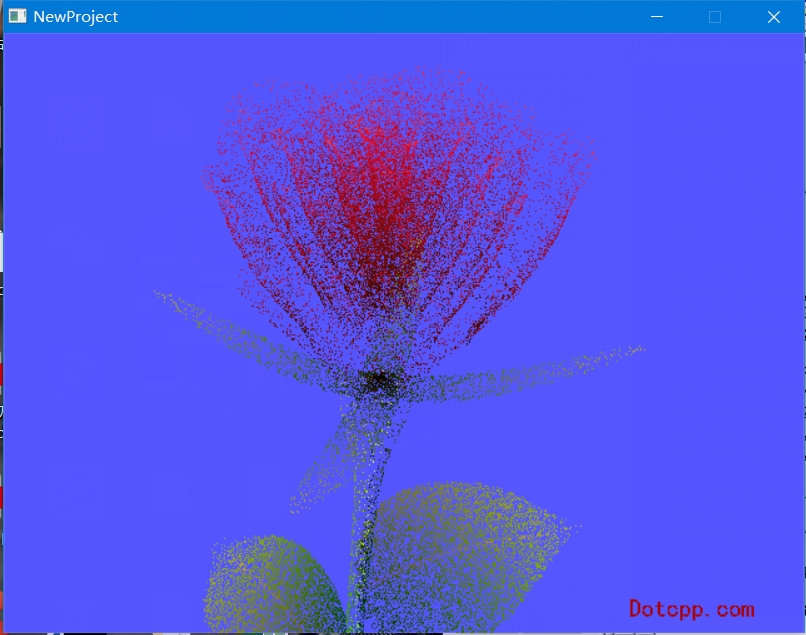
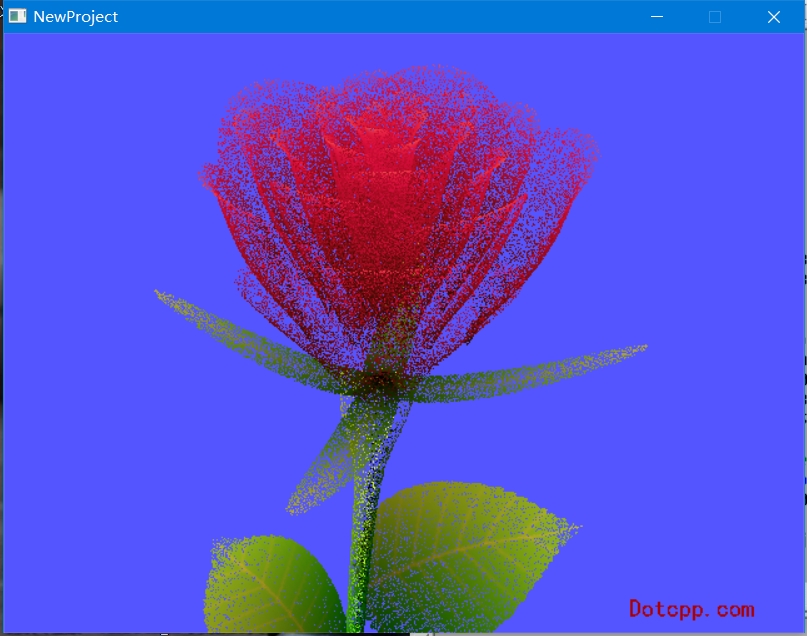
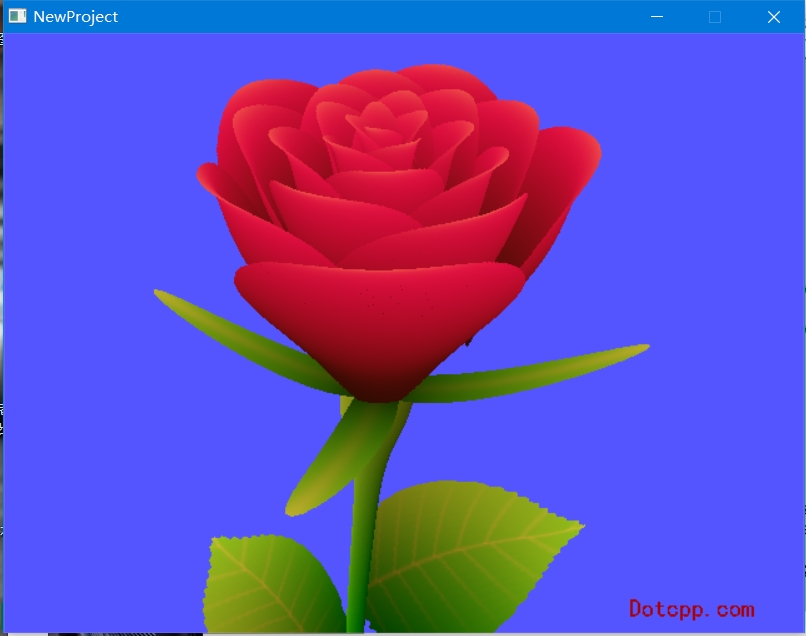
三、代码思路
1.引入easyx头文件
#include <easyx.h>
2.创建背景为亮蓝色的绘图窗口
initgraph(640, 480); setbkcolor(LIGHTBLUE); cleardevice();
3.定义全局变量
introsesize = 500; inth = -250;
4.定义结构体
struct DOT
{
double x;
double y;
double z;
double r;
double g;
};5.计算点
bool calc(double a, double b, double c, DOT& d)
{
double j, n, o, w, z;
......完成
四、完整源码
// 编译环境:VC6.0 / VC2010,EasyX_20210730
// 最后修改:2023-10-6
#include <graphics.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <math.h>
// 定义全局变量
introsesize = 500;
inth = -250;
// 定义结构体
struct DOT
{
double x;
double y;
double z;
double r;// 红色
double g;// 绿色
// b(蓝色) 通过 r 计算
};
// 计算点
bool calc(double a, double b, double c, DOT& d)
{
double j, n, o, w, z;
if (c > 60)// 花柄
{
d.x = sin(a * 7) * (13 + 5 / (0.2 + pow(b * 4, 4))) - sin(b) * 50;
d.y = b * rosesize + 50;
d.z = 625 + cos(a * 7) * (13 + 5 / (0.2 + pow(b * 4, 4))) + b * 400;
d.r = a * 1 - b / 2;
d.g = a;
return true;
}
double A = a * 2 - 1;
double B = b * 2 - 1;
if (A * A + B * B < 1)
{
if (c > 37)// 叶
{
j = (int(c) & 1);
n = j ? 6 : 4;
o = 0.5 / (a + 0.01) + cos(b * 125) * 3 - a * 300;
w = b * h;
d.x = o * cos(n) + w * sin(n) + j * 610 - 390;
d.y = o * sin(n) - w * cos(n) + 550 - j * 350;
d.z = 1180 + cos(B + A) * 99 - j * 300;
d.r = 0.4 - a * 0.1 + pow(1 - B * B, -h * 6) * 0.15 - a * b * 0.4 + cos(a + b) / 5 + pow(cos((o * (a + 1) + (B > 0 ? w : -w)) / 25), 30) * 0.1 * (1 - B * B);
d.g = o / 1000 + 0.7 - o * w * 0.000003;
return true;
}
if (c > 32)// 花萼
{
c = c * 1.16 - 0.15;
o = a * 45 - 20;
w = b * b * h;
z = o * sin(c) + w * cos(c) + 620;
d.x = o * cos(c) - w * sin(c);
d.y = 28 + cos(B * 0.5) * 99 - b * b * b * 60 - z / 2 - h;
d.z = z;
d.r = (b * b * 0.3 + pow((1 - (A * A)), 7) * 0.15 + 0.3) * b;
d.g = b * 0.7;
return true;
}
// 花
o = A * (2 - b) * (80 - c * 2);
w = 99 - cos(A) * 120 - cos(b) * (-h - c * 4.9) + cos(pow(1 - b, 7)) * 50 + c * 2;
z = o * sin(c) + w * cos(c) + 700;
d.x = o * cos(c) - w * sin(c);
d.y = B * 99 - cos(pow(b, 7)) * 50 - c / 3 - z / 1.35 + 450;
d.z = z;
d.r = (1 - b / 1.2) * 0.9 + a * 0.1;
d.g = pow((1 - b), 20) / 4 + 0.05;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 主函数
int main()
{
// 定义变量
short* zBuffer;
intx, y, z, zBufferIndex;
DOTdot;
// 初始化
initgraph(640, 480);// 创建绘图窗口
setbkcolor(LIGHTBLUE);// 设置背景色为亮蓝色
cleardevice();// 清屏
setcolor(RED);
setbkmode(TRANSPARENT);
settextstyle(20,0,"楷体");
outtextxy(450, 430, "");
outtextxy(500, 450, "Dotcpp.com");
// 初始化 z-buffer
zBuffer = new short[rosesize * rosesize];
memset(zBuffer, 0, sizeof(short) * rosesize * rosesize);
for (int j = 0; j < 2000 && !_kbhit(); j++)// 按任意键退出
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)// 减少是否有按键的判断
if (calc(double(rand()) / RAND_MAX, double(rand()) / RAND_MAX, rand() % 46 / 0.74, dot))
{
z = int(dot.z + 0.5);
x = int(dot.x * rosesize / z - h + 0.5);
y = int(dot.y * rosesize / z - h + 0.5);
if (y >= rosesize) continue;
zBufferIndex = y * rosesize + x;
if (!zBuffer[zBufferIndex] || zBuffer[zBufferIndex] > z)
{
zBuffer[zBufferIndex] = z;
// 画点
int r = ~int((dot.r * h));if (r < 0) r = 0;if (r > 255) r = 255;
int g = ~int((dot.g * h));if (g < 0) g = 0;if (g > 255) g = 255;
int b = ~int((dot.r * dot.r * -80));if (b < 0) b = 0;if (b > 255) b = 255;
putpixel(x + 50, y - 20, RGB(r, g, b));
}
}
Sleep(5);
}
// 退出
delete[]zBuffer;
_getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}本文固定URL:https://www.dotcpp.com/course/1269
上一课: